Trends for Embracing Warehouse Automation
Focused on improving capacity utilization, speeding up order cycle times and picking more lines per hour, companies are investing in technology that helps them achieve these goals—and more. As the labor shortage drags on, the number of companies taking this route continues to increase—all with an eye on balancing human workforces with the power of warehouse automation.
Focused on enhancing capacity utilization, expediting order cycle times, and increasing the number of lines picked per hour, organizations are investing in technologies that facilitate these objectives and beyond. As the labor shortage persists, more companies are opting for this approach, all while aiming to strike a balance between human resources and warehouse automation.
To delve deeper into these evolving trends, Peerless Research Group and Modern Materials Handling conducted a comprehensive assessment of the adoption and intentions regarding automation systems and solutions in warehouse and distribution center operations.
The survey conducted among Modern's readers investigates the critical factors and features deemed significant when assessing automation systems and solutions, the deployment of automation within warehouses, and the areas where readers aim to enhance operations over the next two years. Additionally, the survey explores the utilization and plans for equipment in facilities and the anticipated investments companies intend to make in warehouse automation this year.
Overview:
Modern Materials Handling's "2024 Automation Solutions Study" was conducted in November 2023, garnering 155 usable responses from professionals engaged in materials handling and fulfillment operations.
The survey respondents represent various industries, including food, beverage, tobacco, industrial machinery, electrical equipment, plastics, and rubber. A significant portion of respondents work in warehouses or distribution centers, while others are in manufacturing, corporate headquarters, or warehouses supporting manufacturing.
Key Findings:
Regarding warehouse space, respondents work in warehouses ranging from smaller facilities under 50,000 square feet to larger ones spanning 250,000 square feet or more, with an average size of 152,206 square feet. Most facilities have fewer than 100 employees, with an average of 1,032 employees.
Evaluation of Automation Systems:
When evaluating automation systems, respondents prioritize durability, reliability, uptime, total cost of ownership, return on investment, and maintenance costs. Other factors include support and service response time, parts availability, integration with existing equipment, purchase price, scalability, warranty, and turnkey solutions.
Drivers for Automation:
Companies seek automation to enhance capacity utilization, picking efficiency, order fulfillment speed, and order accuracy. Other drivers include meeting e-commerce demands, compensating for labor shortages, staying competitive, and supporting new market strategies.
Manual vs. Automated Processes:
While some processes like conveyance and reporting are largely automated, many warehouses still handle core tasks manually, including storage, packaging, retrieval, replenishment, and order fulfillment.
Source: Peerless Research Group (PRG)
INTRODUCING OUR NEW LOAD-X GOODS-TO-PERSON AUTOMATED STORAGE SYSTEM.
Future Plans:
Over the next two years, companies aim to improve various aspects of their operations, including capacity utilization, picking efficiency, turnover reduction, throughput, order accuracy, and order cycle time. Some respondents plan to adjust their purchasing plans for warehouse and distribution center solutions, while others remain undecided.
Order Fulfillment Activities:
Current order fulfillment activities include warehousing, storage, case and mixed case fulfillment, order customization, repacking, value-added services, pallet load fulfillment, and individual pick, pack, and ship for both e-commerce and wholesale distribution.
Investment in Equipment and Solutions:
Companies continue to invest in both conventional and automated equipment, with lift trucks, dock equipment, rack and shelving being commonly used conventional equipment. Automated solutions such as weighing, cubing, dimensioning equipment, conveyor, sortation systems, mobile collaborative robotics, A-frame picking technologies, picking robotics, palletizing robotics, barcode scanners, mobile or wireless technologies, and voice-directed picking technologies are also gaining traction.
Supply Chain Software Usage:
Warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), warehouse control systems (WCS), and other supply chain execution (SCE) and supply chain management (SCM) solutions are widely used to streamline operations.
Spending Trends:
On average, companies estimate spending $1.67 million on materials handling equipment and solutions in 2023, with a majority allocating budgets for various expenditure ranges. Purchases are commonly made directly from manufacturers, though some companies work with distributors/dealers or systems integrators.
Future Outlook:
Companies anticipate continued investments and collaborations with integrators, distributors/dealers, and manufacturers in the realm of warehouse and distribution center solutions.
By embracing automation and technology, companies are poised to optimize their operations, adapt to market demands, and navigate the challenges posed by labor shortages in the evolving landscape of warehouse and distribution center management.
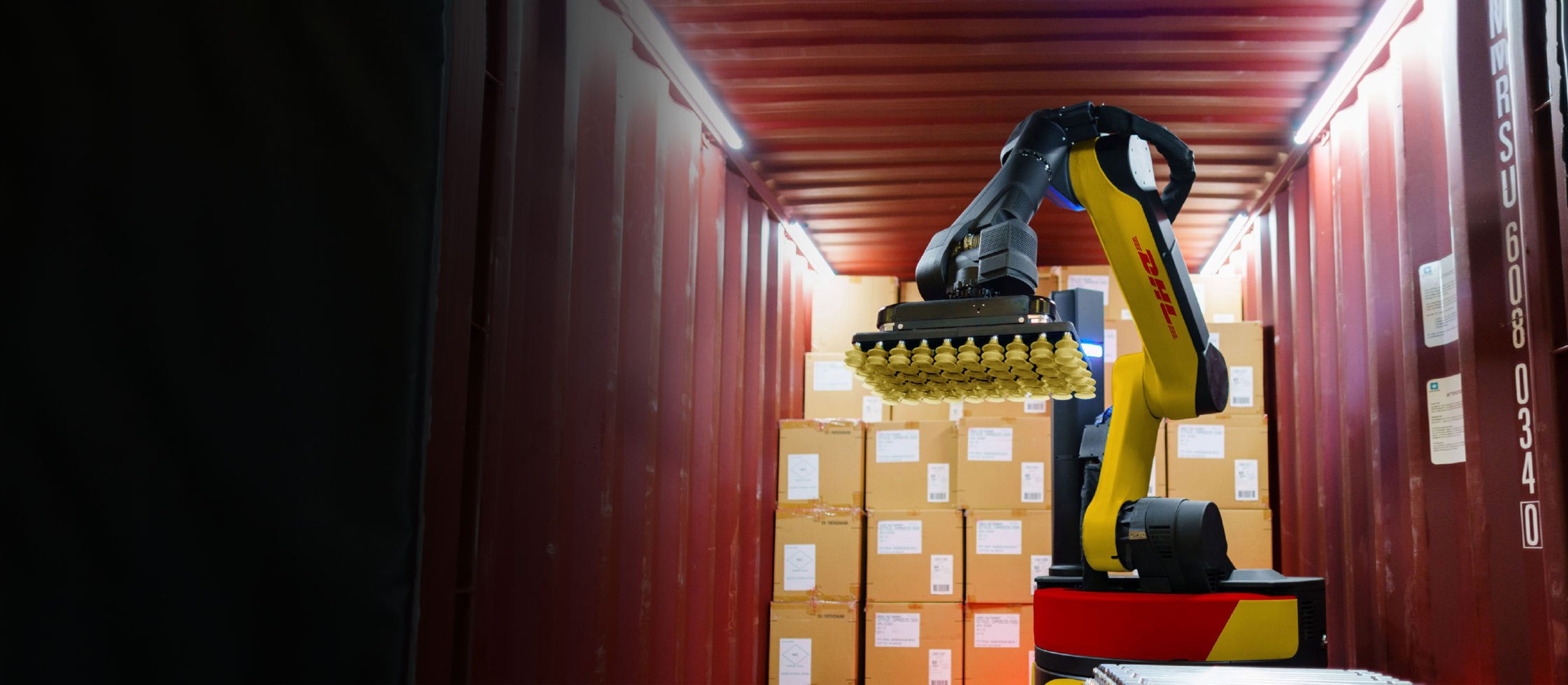








































Host Evan Reiser welcomes Sally Miller, Global Chief Information Officer at DHL Supply Chain.